Exec的源码乱看与杂七杂八
Java面向对象
Java面向对象有三大特点:封装,继承,多态。
- 封装是把数据和操作隐藏到对象里面,无法看到对象是什么实现的,对象只向外界暴露最简单的接口。封装通过private,default,protected和public来控制封装和访问。
- 继承是子类复用父类的代码。使得子类具有父类的全部行为和特性,但也能修改父类的行为和特性或者拓展自己新的行为和特性。java的类是单继承,接口是多继承。
- 多态使得不同的子类对同一个请求可是有不同的响应,并且调用者不需要知道其实现是哪个子类的版本。多态分为编译时多态(重载)和运行时多态(重写)。
七层协议
应用层,表示层,会话层,传输层,网络层,数据链路层,物理层
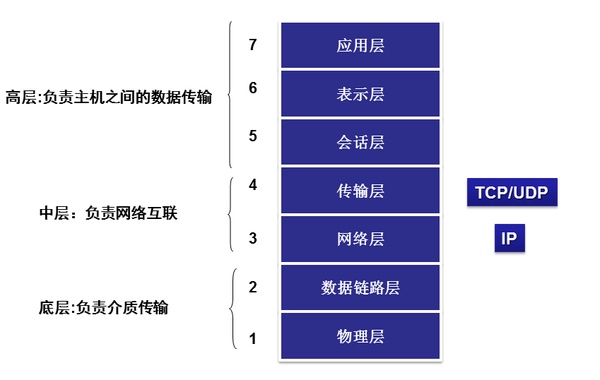
| 7 | 应用层 | 例如HTTP、SMTP、SNMP、FTP、Telnet、SIP、SSH、NFS、RTSP、XMPP、Whois、ENRP |
| 6 | 表示层 | 例如XDR、ASN.1、SMB、AFP、NCP |
| 5 | 会话层 | 例如ASAP、TLS、SSH、ISO 8327 / CCITT X.225、RPC、NetBIOS、ASP、Winsock、BSD sockets |
| 4 | 传输层 | 例如TCP、UDP、RTP、SCTP、SPX、ATP、IL |
| 3 | 网络层 | 例如IP、ICMP、IGMP、IPX、BGP、OSPF、RIP、IGRP、EIGRP、ARP、RARP、 X.25 |
| 2 | 数据链路层 | 例如以太网、令牌环、HDLC、帧中继、ISDN、ATM、IEEE 802.11、FDDI、PPP |
| 1 | 物理层 | 例如线路、无线电、光纤、信鸽 |
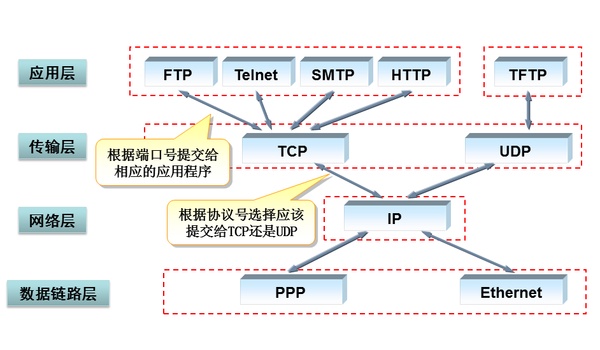
TCP/UDP协议,HTTP/FTP使用场景
TCP是面向连接的,提供可靠的,即数据是按序不丢失到达的。为了保证可靠,使用了超时重发等机制,成本较大。
UDP提供的是不可靠的数据传输,不需要创建连接,不使用超时重发等机制,成本低,速度快。
HTTP用于传输超文本的(不是很理解超文本是啥,html?又好像不是)
FTP是用来传输文件的
java爬虫两件套
进行http请求当然是apache的http包,分析html可以用jsoup,分析json的就很多了。
乐观锁与CAS
乐观锁是相对于悲观锁而言的。乐观锁认为并发操作一般不会发生冲突,先尝试进行操作,发生冲突了才返回错误信息让用户判断。而CAS是乐观锁的一种实现。
线程池的优缺点与线程数变化
线程池能集中控制线程,限制线程数量,减少线程创建销毁的成本等。但是如果使用了一些线程数动态浮动的线程池,仍然有可能会线程爆炸。线程池默认一开始是没有线程的,当有任务进来的时候,就创建一个线程来执行,直到线程数达到核心线程数之后,新的任务就会先放到队列里,直到队列满了,才创建新的线程。又直到线程数达到最大线程数时,进行任务拒绝处理。任务拒绝处理策略有四种:直接丢弃,丢掉队列里最旧的任务,抛异常,用添加任务的线程执行此任务。
常用的设计模式
创建型模式:单例模式,工厂模式,构造者模式
结构型模式:代理模式
行为型模式:观察者模式
Exec源码
先来回顾一下Exec包是怎么用的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
CommandLine commandLine = new CommandLine("xxx.exe");
DefaultExecuteResultHandler resultHandler = new DefaultExecuteResultHandler();
ExecuteWatchdog watchdog = new ExecuteWatchdog(60*1000);
Executor executor = new DefaultExecutor();
executor.setExitValue(1);
executor.setWatchdog(watchdog);
//在执行方法添加DefaultExecuteResultHandler对象,这样方法就不会阻塞了
executor.execute(commandLine, resultHandler);
//waitFor方法会阻塞直到命令执行完成或者到监控狗指定的时间
resultHandler.waitFor();
}
最最重要的就是执行器类:DefaultExecutor。接下来看看DefaultExecutor的源码,从execute方法切入。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170public class MyDefaultExecutor {
private ExecuteStreamHandler streamHandler = new PumpStreamHandler();//应该是用来处理命令执行时候的流
private File workingDirectory = new File(".");//命令执行的当前路径
private ExecuteWatchdog watchdog;
private int[] exitValues = new int[0];
private final CommandLauncher launcher = CommandLauncherFactory.createVMLauncher();
private ProcessDestroyer processDestroyer;//运行执行摧毁器
private Thread executorThread;//执行线程
private IOException exceptionCaught = null;
public int execute(CommandLine command) throws ExecuteException, IOException {
return execute(command, (Map) null);
}
public int execute(CommandLine command, Map<String, String> environment) throws ExecuteException, IOException {
if (this.workingDirectory != null && !this.workingDirectory.exists()) {
throw new IOException(this.workingDirectory + " doesn't exist.");
} else {
//利用executeInternal方法执行,会阻塞
return executeInternal(command, environment, this.workingDirectory, this.streamHandler);
}
}
public void execute(CommandLine command, ExecuteResultHandler handler) throws ExecuteException, IOException {
this.execute(command, null, handler);
}
public void execute(final CommandLine command, final Map<String, String> environment, final ExecuteResultHandler handler) throws ExecuteException, IOException {
if (this.workingDirectory != null && !this.workingDirectory.exists()) {
throw new IOException(this.workingDirectory + " doesn't exist.");
} else {
if (this.watchdog != null) {
//设置运行执行未开始?
this.watchdog.setProcessNotStarted();
}
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int exitValue = -559038737;
try {
//同样利用executeInternal方法执行,会阻塞。但不怕,比较在线程里
exitValue = MyDefaultExecutor.this.executeInternal(command, environment, DefaultExecutor.this.workingDirectory, DefaultExecutor.this.streamHandler);
//执行完后,调用handler的onProcessComplete方法,handler就可以从waitFor方法里返回
handler.onProcessComplete(exitValue);
} catch (ExecuteException var3) {
//异常什么的都记录到handler里
handler.onProcessFailed(var3);
} catch (Exception var4) {
handler.onProcessFailed(new ExecuteException("Execution failed", exitValue, var4));
}
}
};
//创建一个Thread然后start,就不阻塞了
this.executorThread = this.createThread(runnable, "Exec Default Executor");
this.getExecutorThread().start();
}
}
protected Thread createThread(Runnable runnable, String name) {
return new Thread(runnable, name);
}
//执行命令,会阻塞,因为调用了process.waitFor()
private int executeInternal(CommandLine command, Map<String, String> environment, File dir, ExecuteStreamHandler streams) throws IOException {
this.setExceptionCaught(null);
//创建一个运行之类的对象
Process process = this.launch(command, environment, dir);
try {
//往流处理器里设置这个运行对象
streams.setProcessInputStream(process.getOutputStream());
streams.setProcessOutputStream(process.getInputStream());
streams.setProcessErrorStream(process.getErrorStream());
} catch (IOException var29) {
process.destroy();
throw var29;
}
//启动用于处理流处理器的输入输出异常流的三个线程
//(又是三个新创建的线程啊,怎么没有用线程池呢)
streams.start();
int var7;
try {
if (getProcessDestroyer() != null) {
//往运行摧毁器里添加这处理(运行摧毁器会按照监控狗来摧毁运行吗?)
getProcessDestroyer().add(process);
}
if (this.watchdog != null) {
//监控狗执行运行?
this.watchdog.start(process);
}
int exitValue = -559038737;
try {
//执行后等待完成,并获取离开值
exitValue = process.waitFor();
} catch (InterruptedException var27) {
process.destroy();
} finally {
Thread.interrupted();
}
if (this.watchdog != null) {
//停止监控狗
this.watchdog.stop();
}
try {
//关闭三个流的线程
streams.stop();
} catch (IOException var26) {
this.setExceptionCaught(var26);
}
//关闭各种流
closeProcessStreams(process);
if (this.getExceptionCaught() != null) {
throw this.getExceptionCaught();
}
if (this.watchdog != null) {
try {
this.watchdog.checkException();
} catch (IOException var24) {
throw var24;
} catch (Exception var25) {
throw new IOException(var25.getMessage());
}
}
if (this.isFailure(exitValue)) {
throw new ExecuteException("Process exited with an error: " + exitValue, exitValue);
}
var7 = exitValue;
} finally {
if (this.getProcessDestroyer() != null) {
this.getProcessDestroyer().remove(process);
}
}
return var7;
}
private void closeProcessStreams(Process process) {
try {
process.getInputStream().close();
} catch (IOException var5) {
this.setExceptionCaught(var5);
}
try {
process.getOutputStream().close();
} catch (IOException var4) {
this.setExceptionCaught(var4);
}
try {
process.getErrorStream().close();
} catch (IOException var3) {
this.setExceptionCaught(var3);
}
}
//还有一些setget方法
}
参考文章: